Resources : C-NRPP Documents
- Home
- Resources : C-NRPP Documents
Consumer-Grade Electronic Radon Monitors
Over the past several years, consumer-grade electronic radon monitors have become more widely available. The C-NRPP offers an independent performance report comparing these devices. CNRPP
Key points:
- These monitors are designed for homeowners, not for professional use by certified measurement providers. CNRPP
- You should use the device for at least 3 months, preferably during the heating season, to obtain a meaningful long-term average. Short-term readings can be misleading. CNRPP
- When purchasing a monitor, choose one that has passed C-NRPP performance testing to ensure reliability. Canada
Steps to Reduce Radon
To reduce RADON, first test your home using a long-term kit or certified device placed in a regularly used area.
If the level is above 200 Bq/m³, hire a C-NRPP certified professional to install a proper mitigation system, usually a sub-slab depressurization system that vents RADON safely outdoors.
After installation, test again to confirm the system’s effectiveness and maintain low levels over time.
Following these steps helps ensure a safe and healthy indoor environment for your family.
Radon and New Builds or New-to-You Homes
All new homes should still be tested during the first heating season - building codes and rough-ins alone don’t guarantee low radon levels. The National Building Code of Canada and many provincial codes require a radon-control rough-in (e.g., granular layer, sealed membrane, rough-in pipe) in new construction. In Ontario, warranties may cover mitigation if levels exceed the guideline. If you’re building or moving into a new home, ask for a builder who uses a C-NRPP “CRNCH”-certified professional to ensure proper radon-control measures. c-nrpp.ca
C-NRPP Code of Ethics and Professional Standards
All C-NRPP certified radon professionals must follow strict ethical and technical standards. They are required to maintain up-to-date training, perform work within their certified expertise, and operate with integrity and confidentiality. Each project must include the professional’s certification number and follow approved Health Canada and C-NRPP protocols for testing and mitigation. Certified mitigators must also provide reasonable warranties, carry liability and errors-and-omissions insurance, and comply with ,national and provincial codes. Violations may lead to disciplinary action or certification revocation, ensuring trustworthy, high-quality service for Canadian homeowners.
C-NRPP Quality Assurance and Control (QA/QC) Standards
All C-NRPP certified radon professionals must follow strict Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) procedures to ensure accurate, consistent, and reliable testing. These include device calibration, duplicate and blank testing, spike performance tests, and maintaining detailed QA/QC records. Professionals must use only C-NRPP approved measurement devices and follow Health Canada’s measurement protocols. Regular calibration, documentation, and corrective actions are required to maintain certification and protect public health by ensuring radon measurements remain precise and trustworthy.
Short-Term RADON Measurement Protocol
This C-NRPP guideline provides standards for short-term radon testing (minimum 48 hours, up to 90 days). Tests must be performed using C-NRPP approved devices and follow Health Canada placement procedures - usually in the lowest occupied level of a home. During testing, closed-house conditions must be maintained to ensure accuracy. A post-mitigation test verifies system performance, and a long-term follow-up test is strongly recommended. Reports must include the professional’s C-NRPP ID, device details, test duration, and radon results in Bq/m³. Proper records should be kept for at least 10 years.
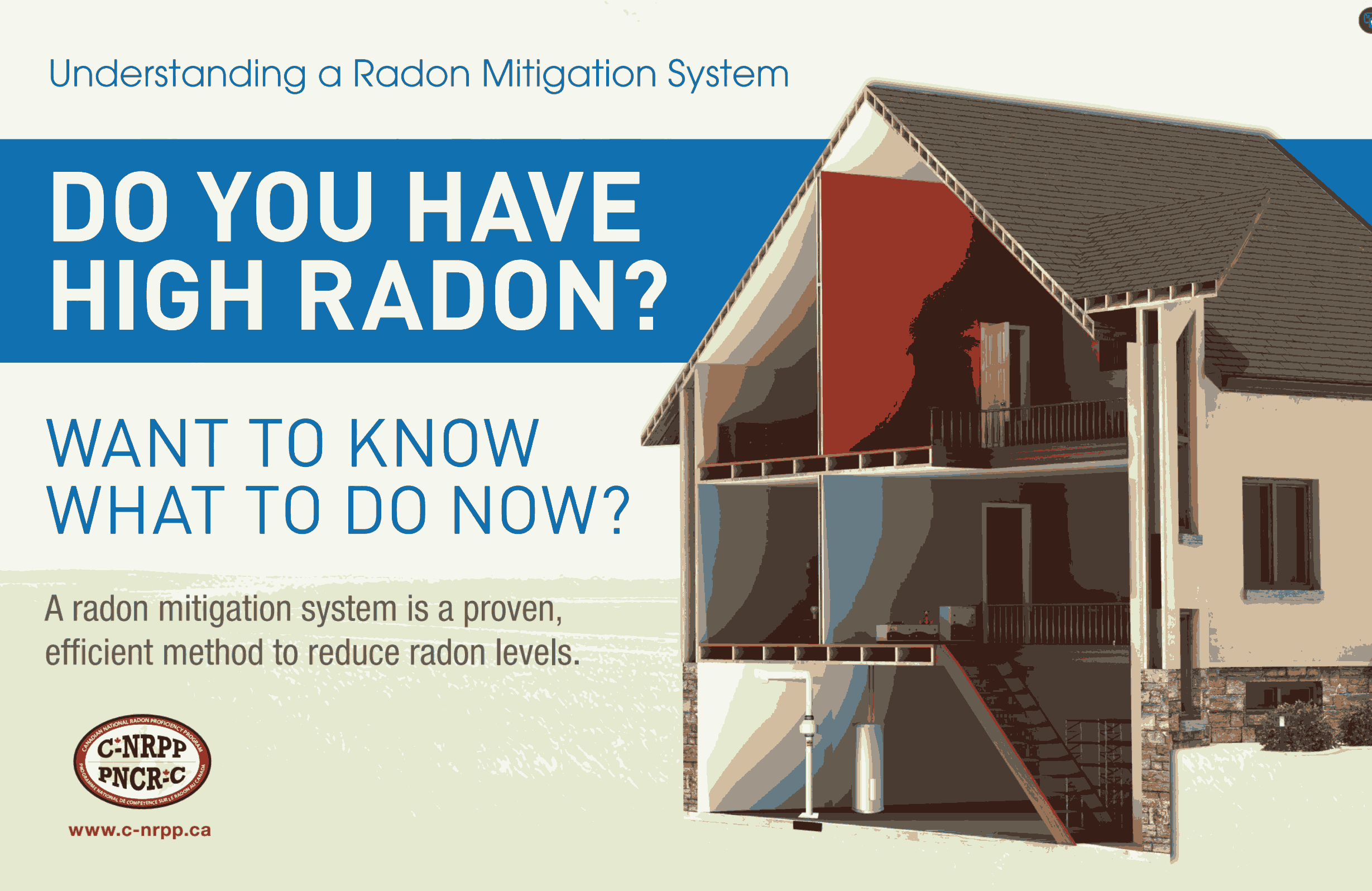
Understanding a RADON Mitigation System
If your home tests high for RADON, hire a C-NRPP Certified Professional for proper system design and installation. The most effective method is Active Soil Depressurization (ASD), which uses a fan and vent pipe to draw RADON from beneath the foundation and exhaust it safely outdoors. A professional ensures the correct fan size, suction point, and air pathway. Once operating, the system typically reduces indoor RADON to outdoor-air levels, often improving basement humidity and air quality as well. The fan should remain on at all times for continuous protection.
RADON Control in New Homes (C-NRPP Technical Bulletin 2024)
All new homes in Canada should include radon control measures during construction. The National Building Code 2020 requires a sealed sub-slab membrane, granular drainage layer, sealed sump pit, and radon rough-in pipe. Builders are encouraged to follow best practices from CAN/CGSB 149.11-2024, such as proper perimeter sealing, clear labeling, and planned fan installation space. Homeowners should test after construction and again three years later to confirm safety. Working with a C-NRPP certified professional ensures low-radon results and compliance with Health Canada’s standards.